Vertebral fracture
A vertebral fracture can be a fracture of the vertebral body, vertebral arch or spinous process. In the case of a vertebral body fracture caused by crushing, the vertebral body collapses causing a burst or teardrop fracture, rupturing the anterior or posterior edge of the vertebra.
The most common location is in the last dorsal or first lumbar vertebra. In the case of the vertebra being displaced in an anterior direction, the result is spondylolisthesis or spondylolysis, the former of which can be stable or unstable and the latter stable. Fracture-dislocation can also occur after suffering some type of trauma. Some vertebral fractures can occur without being caused by a high-energy mechanism, for example, a bending movement can produce a wedge fracture, as is the case in patients with osteoporosis.
Symptoms of Vertebral fracture
Pain can sometimes go unnoticed, but is usually evident on palpation or percussion of the spinous processes. Muscle contraction is evident, resulting in limited mobility and the adoption of kyphotic postures. Any neurological signs, such as paresis, hypoesthesia or osteo-tendon reflex disturbance, are indicative that there is some degree of compression with neurological compromise, for which decompression is necessary.
Spinal compression fractures - Orthotic Treatment
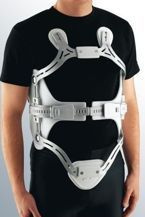
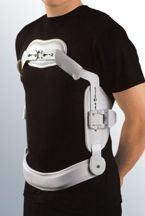
The orthotic treatment of spinal fractures by means of braces with varying degrees of immobilisation and unloading are useful if there are no neurological signs present. If there are, decompression or alignment of the physiological curves would be necessary, and this can be carried out by using orthotic methods, as is also the case with serious CT, burns or other associated disorders in which surgery to fix and stabilise the affected vertebral segment can be delayed. Stabilisation and immobilisation orthoses for the treatment of vertebral fractures need to be made from rigid materials (lumbar and dorsolumbar braces featuring metal or thermoplastic reinforcements) and include folding braces, Jewett hyperextension or cruciform braces, which, by means of supports located on the chest, pelvis and dorsolumbar transit area, exert compression forces that modify the physiological curve, enabling hyperkyphosis realignment and producing a hyperextension that prevents compression and vertebral wedging.