Back pain - causes and treatment options
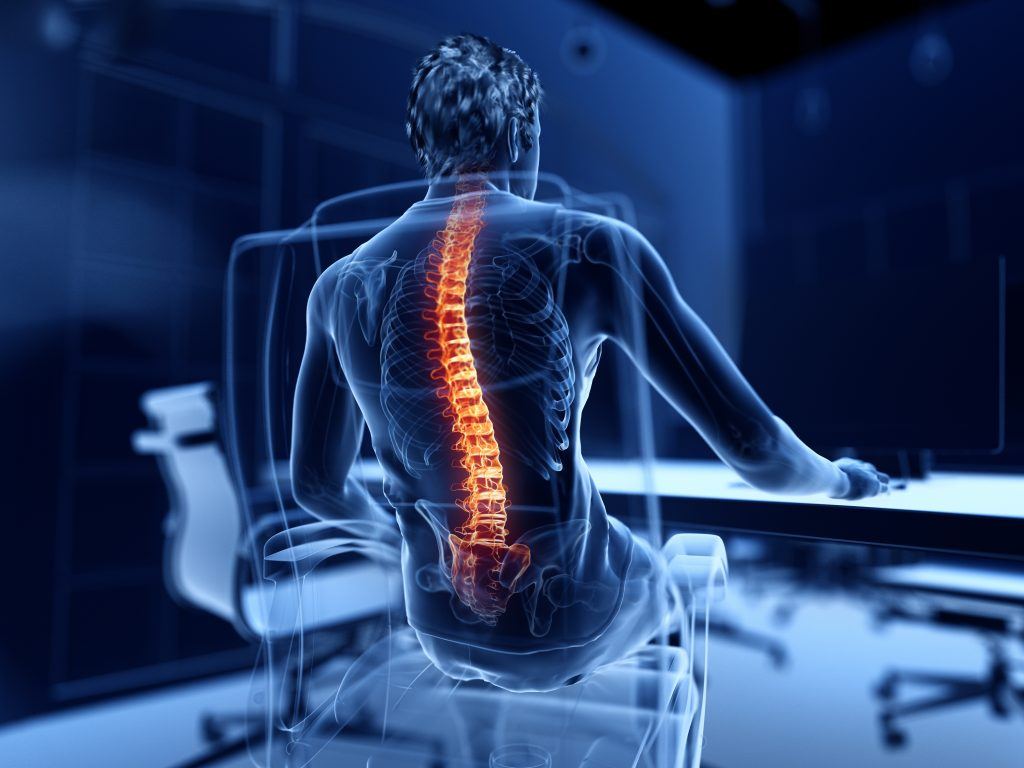
Back pain is probably one of the most common reasons for work absence. No matter if the pain is acute or chronic, it can significantly reduce your quality of life (Back pain). But what exactly causes it and what treatment options are there? Continue reading to learn medical advice on treating back pain.
What causes back pain?
Back pain is one of the most common reasons for work absence and for seeking treatments and medical advice. Whether you have physically demanding work or have a desk job behind a computer monitor, you might experience some degree of back pain, which is uncomfortable and may even lead to more serious conditions.
Back pain can be caused by a number of underlying factors, including strains, conditions of the joints and spine, issues pertaining to movement and posture, as well as a number of other conditions that can take their toll on your back.
Back pain caused by strains
Strain on the back and spine is one of the most common reasons for back pain, and can lead to other potential problems. This can lead to lower back pain and is often caused by lifting something improperly or something that is too heavy - however, making abrupt or awkward movements may also cause strain, especially if you’re in poor physical condition and your back muscles are not used to this (Back pain).
Conditions of the joints and spine
Certain conditions affecting your spine, joints and back muscles can also lead to significant back pain - these tend to include:
- Conditions affecting disks: the disks found between each vertebra help to cushion the spine - if one of these disks ruptures or bulges outward, it can put significant pressure on the surrounding nerves and consequently cause pain (Back pain). If you experience lower back pain as well as pain around the buttocks and the back of the leg, you might have a sciatica, which is caused by a herniated disk (What is causing this pain in my back?).
- Conditions affecting disks: the disks found between each vertebra help to cushion the spine - if one of these disks ruptures or bulges outward, it can put significant pressure on the surrounding nerves and consequently cause pain (Back pain). If you experience lower back pain as well as pain around the buttocks and the back of the leg, you might have a sciatica, which is caused by a herniated disk (What is causing this pain in my back?).
- Conditions of the bones: certain bone conditions may also lead to back pain - most commonly osteoarthritis and osteoporosis. Osteoarthritis of the spine occurs when disks between the vertebrae begin to stiffen and shrink, which can pinch the nerves. Osteoporosis on the other hand makes bones brittle, which increases the risk of compression fractures (What is causing this pain in my back?).
- Conditions affecting the nerves: conditions such as a tumor that pinches a nerve on the back and infections of the spine all affect the nerves. A tumor, such as vertebral tumors, osteoid osteomas and osteoblastomas can spread to the spine and cause significant pressure and back pain (Vertebral tumor). Certain infections, such as pelvic inflammatory disease, kidney infections and shingles can also cause significant back pain.
Irregularities in movement and posture
Although physical activities like lifting heavy weights can cause potential back pain, it may also be brought on by factors as simple as bad posture and irregular movements. Bad posture can result from bending awkwardly and sitting for extended periods of time, as well as straining the neck forwards, like when using a computer (What is causing this pain in my back?). Certain spinal irregularities can also affect posture, like scoliosis, which causes the spine to bend to the side and may also cause back pain (Back pain).
Other conditions that may cause back pain
Back pain can be caused by a number of conditions - some of which don’t necessarily begin at the back. If you put significant strain on your spine (physically demanding work or exercise), lead a sedentary lifestyle, are obese, pregnant, are prone to diseases, or are simply older, then you may also experieience back pain (Back pain).
What are the types of back pain?
Back pain can be categorized into 2 groups, based on severity and location on the spine. The pain can either be acute or chronic - acute back pain is usually short-term and sudden, and can be caused by overstretching the lumbar or back muscles. Chronic pain is often caused by recurring conditions that can make everyday life difficult, such as a bulging disk or osteoporosis (What is causing this pain in my back?).
The spine is divided up into 3 primary regions, which include the cervical region (vertebrae of the neck), the thoracic region (including the vertebrae of the upper back), as well as the lumbar religion (vertebrae of the lower back) (Back pain). The most susceptible areas to back pain tend to be the lumbar and cervical parts, since they’re the most often used (Types of back pain). If you experience thoracic back pain, it’s important that you seek medical advice if it doesn’t pass, you notice any deformities, experience severe stiffness and a number of other conditions. In most cases, pain in this area may be caused by an injury or a chronic condition (Types of back pain).
How to treat various back pain?
When it comes to treating back pain, you need to take into account which part of the back is affected, the type of pain (acute or chronic), and what might be causing it. If you suffer from acute back pain caused by sitting a bit too long on your computer, then you may want to have a go at getting a professional massage or physical therapy. You should also ask your doctor if a back brace is right for you. A well-chosen back brace can help fix bad posture and force your back into its natural position - for more information and where to find a reliable back brace, visit our page e-MedicalBroker.com. In order to avoid acute back pain caused by minor strains and poor posture, you may want to introduce a back pain exercise and stretching regimen. Here are some stretches you may want to include:
- Knee to chest stretch: your starting position should be on your back with your feet flat on the floor and your knees bent. Pull one leg to your chest and keep it there for 5 seconds - while your spine is kept on the floor. Make sure to repeat the process with the other leg and maintain a floor hold at all times (Types of back pain).
- Bridge exercise: start by laying on your back with your feet flat on the floor- squeeze your stomach muscles and glutes and lift your hips up, along with the rest of your body, in order to form a straight line. Keep this position and maintain the squeeze on the abdominal muscles for up to 3 breaths and repeat this exercise at least 5 times. While you do so, keep your feet flat on the ground and try not to shift their position (Types of back pain).
- Cat stretch: begin this stretch on your hands and knees. Maintaining your starting position, slowly arch your back upward and avoid focusing on your abdominal muscles. Slowly lower your back and allow for your midsection to drop. Repeat this stretch at least 3 times a day (Types of back pain).
If however, your back pain is chronic and is caused by more serious conditions, such as cancer, disk bulges and deformations, you may be required to undergo special treatment options. These treatments may be surgery, physical therapy, certain medication, cortisone injections (to help reduce inflammation around the spinal cord), transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) (electrical shocks sent throughout your body to help it block pain signals), and back braces (What is causing this pain in my back?). Although surgery for treating back pain is rare, it does happen - most often in cases when treating fused vertebrae, when inserting an artificial disk, during discectomies, or when removing part of the vertebrae (What is causing this pain in my back?).
How can back braces help treat back pain?
Just like when treating acute back pain, back braces can also be used for mitigating chronic pain and keeping postoperative sutures in place. They activate the abdominal muscles and not only force the wearer to maintain correct posture, but also stabilize the spine in the lumbar region, and help to alleviate it to some extent. If you’re considering looking for a reliable back brace, it is vital that you consult with your doctor and ask for medical advice on which model to choose. A trained specialist will be able to recommend the right back pain brace for your condition, in order to alleviate the pain and get you back on your feet in no time.
Sources:
- “Vertebral tumor”, Mayo Clinic Staff, May 16, 2018, https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/vertebral-tumor/symptoms-causes/syc-20350123#:~:text=Vertebral%20tumors%20are%20also%20known,%2C%20breast%2C%20lung%20or%20kidney
- “Back pain”, Mayo Clinic Staff, Aug. 04, 2018 https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/back-pain/symptoms-causes/syc-20369906#:~:text=Conditions%20commonly%20linked%20to%20back,can%20cause%20painful%20muscle%20spasms
- “What is causing this pain in my back?”, James McIntosh, February 23, 2017 https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/172943
- “Types of Back Pain”, WCM Center for Comprehensive Spine Care, 2020 https://comprehensivespine.weillcornell.org/conditions-we-treat/back-pain/types-of-back-pain/