Recommended

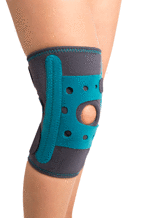
Knee support with patella silicone ring and additional straps Genumedi plus medi
85,00 EUR incl. VAT/1piece

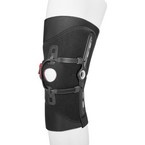
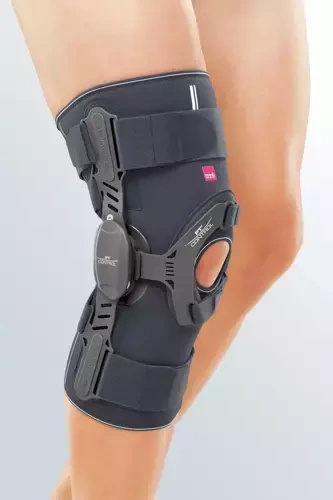
Knee brace promoting muscular balance in cases of patellar lateralisation Genumedi PT
90,00 EUR incl. VAT/1piece

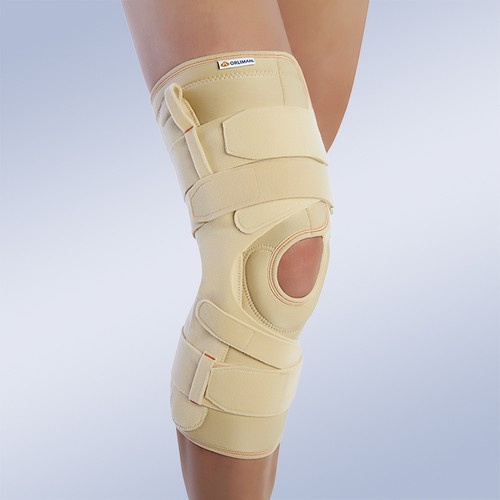
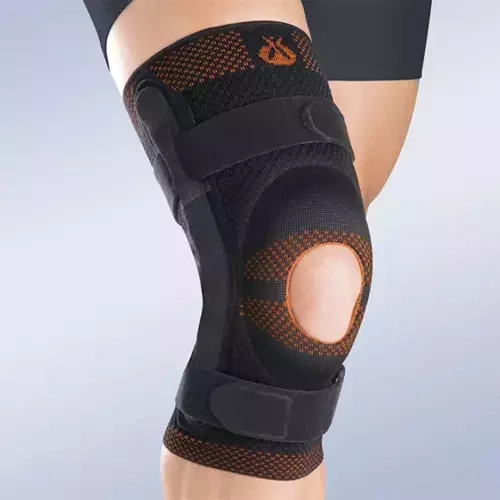
Orliman Rodisil opened patella knee brace with polycentric reinforcements
113,00 EUR incl. VAT/1piece